Anti-Inflammation Diet; how to get rid of inflammation.
The term inflammation is used often and by many, but most people do not know what it actually means.
Inflammation is known to be the root of almost all chronic diseases, so getting Inflammation under control is essential.
In general, inflammation can be caused by many factors such as injuries, allergies, disease, or certain types of food. Foods that can trigger inflammation include carbohydrates, dairy, sugar, trans fats, and gluten.
Continue reading to learn more about inflammation and ways to get rid of it!
Table of Contents:
- What is inflammation?
- What are the top 5 causes of inflammation?
- Best anti-inflammatory foods.
- Fasting and inflammation.
- Foods to avoid on the anti-inflammation diet.
- Tips for reducing inflammation.
- Takeaway.
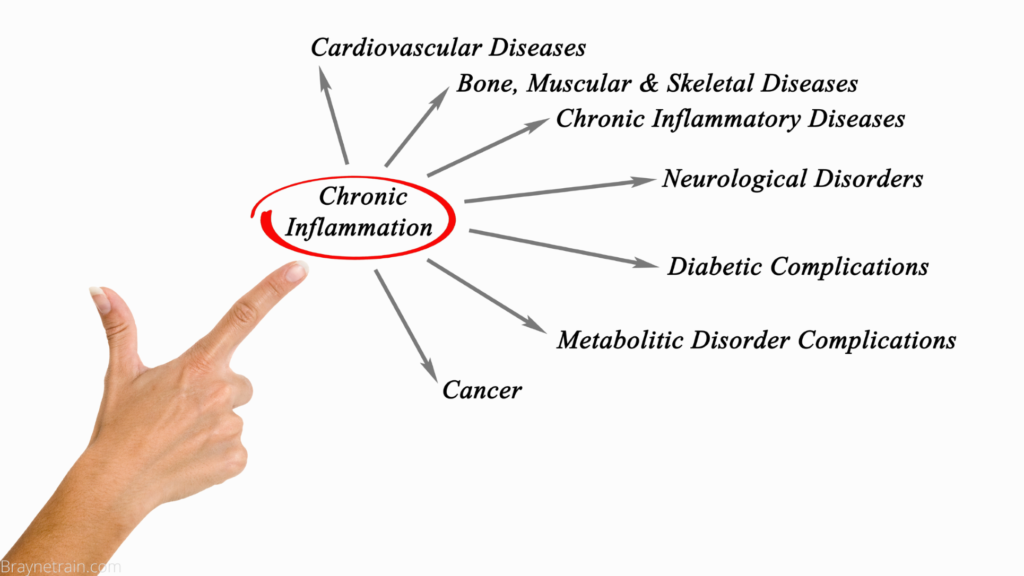
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a vital bodily response to infection and injury, but it can also cause significant pain.
When Inflammation occurs, white blood cells enter the blood and tissues to protect the body from outside invaders. This raises the blood flow to the area of injury or infection and can cause redness and warmth.
In addition, some of the chemicals released during inflammation cause fluid to leak into nearby tissues, resulting in swelling.
This entire process can trigger the nervous system and cause significant pain.
While Inflammation is a necessary and beneficial response in many situations, it can also be the source of considerable discomfort.

what are the Top 5 Causes of Inflammation?
1. Diet
- Processed foods
- Processed foods are high in sugar and carbohydrates, both of which are known to trigger inflammation.
- In addition, processed foods often contain artificial additives and chemicals that contribute to inflammation.
- Sugar
- Sugar has been shown to trigger inflammation in the body.
- In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers found that sugar promotes inflammation by activating immune cells called macrophages.
- Macrophages release pro-inflammatory chemicals that damage tissues and contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
- Fructose
- The sugar that comes from the fruit can cause Inflammation.
- A study published in Journal Lipids in Health & Disease divided 14 participants into three groups and had them consume either fructose, glucose, or sucrose.
- The fructose group had the highest Inflammation markers out of the three groups.
- Dairy
- Dairy products contain a protein called casein, which has been shown to trigger inflammation.
- Soybean oil
- Soybean oil is a common ingredient in processed foods, and it is increasingly being used as a cooking oil. However, new research suggests that soybean oil may trigger inflammation.
- Nuts
- Research has shown that raw nuts can trigger inflammation in the body. So it’s essential to limit the number of raw nuts you consume if you want to avoid inflammation.
- Gluten
- Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. It has been shown to trigger inflammation in the gut, even in people who do not have celiac disease.
- A recent study found that gluten caused inflammation in the guts of healthy people after just one month of being on a gluten-containing diet.
- Alcohol
- Alcohol triggers inflammation by damaging the gut lining, which allows bacteria and other toxins to enter the bloodstream.
- This can cause a systemic inflammatory response, leading to various symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, and digestive problems.

2. Obesity
Obesity is a significant problem in today’s society. It leads to a wide range of health problems, but it also causes inflammation.
Fat cells secrete pro-inflammatory hormones that trigger inflammation.
In addition, obese individuals are more likely to suffer from insulin resistance, which also contributes to inflammation.
The inflammation caused by obesity can damage the body’s tissues and organs and cause many health problems.
To learn more about ways you can lose weight without exercising, click here.

3. Gut inflammation
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria, many of which are essential for good health.
However, an imbalance of bacteria in the gut can lead to inflammation. This inflammation can then spread to other body parts, triggering a widespread inflammatory response.
The inflammation in your gut may be a significant factor for many chronic diseases, such as heart disease and arthritis.
4. Chronic Stress
When the body experiences chronic stress, it goes into fight-or-flight mode and releases cortisol, the stress hormone.
Cortisol is an anti-inflammatory hormone that helps the body cope with stress.
However, if the body experiences chronic stress, it can develop cortisol resistance, which means that it no longer responds to cortisol, and as a result, the body cannot reduce inflammation properly.
Chronic stress can therefore have a negative impact on health.
To learn more about cortisol, click here.

5. Lack of Sleep
Sleep plays a vital role in regulating inflammation.
Lack of sleep can increase your stress levels, which triggers inflammation. So it is vital for you to get enough sleep every night in order to prevent inflammation.
To learn how you can create a nightly routine for better sleep, click here.
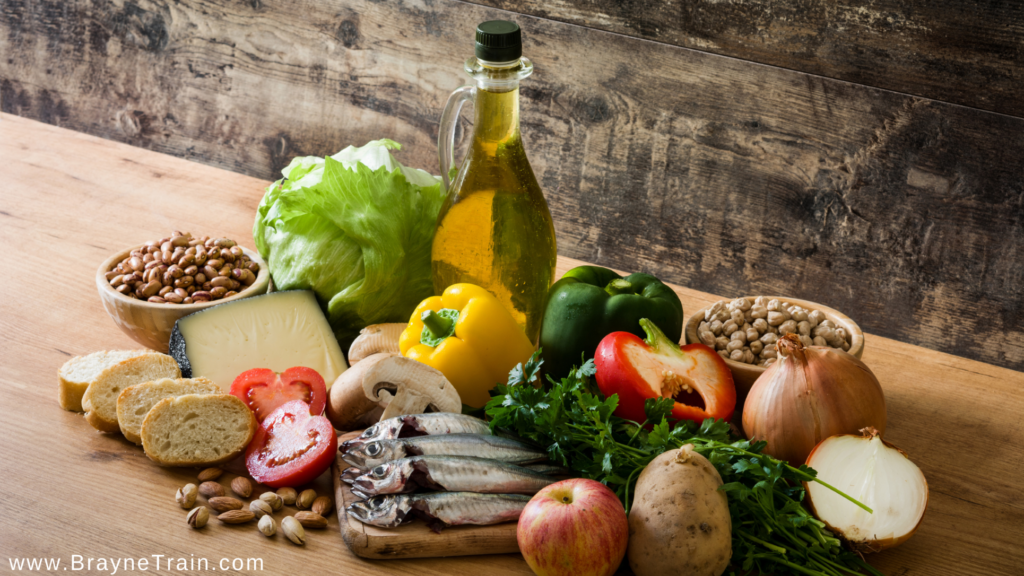

Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods :
- Ginger
- Cabbage (kimchi, raw cabbage, etc.)
- Turmeric
- Berries
- Leafy greens (arugula, spinach, kale, etc.)
- Salmon
- Fatty fish (sardines, mackerel, trout, etc.)
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, etc.)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, etc.)
- Garlic
- Chia Seeds
- Beets
- Pineapple

Intermittent Fasting Helps get rid of Inflammation.
Intermittent fasting improves mitochondria efficiency (cell powerhouses). Also, fasting decreases monocytes which are the leading cause of Inflammation.
A study published in The Journal Cell showed that a 19-hour fast reduced the number of monocytes and macrophages, both of which help create Inflammation.
Therefore, research indicates that intermittent fasting can result in reduced inflammation.
To learn more about intermittent fasting, click here.

Foods To Avoid on the Anti-inflammation Diet:
- Refined carbohydrates (bread, chips, etc.)
- Sugar
- Soybean oil
- Fast food
- Sugary drinks
- Processed meat
- Trans fat
- Dairy
- Raw nuts
- Hydrogenated Oils
Tips for Reducing Inflammation:
- Cook your meat and vegetables in lower heat.
- Avoid combining sugar and fat together when you eat.
- Avoid processed and flashed frozen foods.
- Practice intermittent fasting.
- Practice meditation: meditation lowers stress, and lowering stress helps fight Inflammation.
- Get a good night’s sleep: better sleep helps lower cortisol levels.
- Limit alcohol intake.
- Exercise regularly.
- Try anti-inflammatory diets like clean Keto or the Mediterranean diet, which have proven to help get rid of inflammation.
Takeaway
The root cause of almost all chronic diseases is Inflammation. If you can get Inflammation under control, you can improve your overall health. Many things can cause Inflammation, including diet and lack of sleep. If you suffer from chronic inflammation, do your research, talk to your doctor, and try the tips and tricks we provided in this post, and hopefully, you will soon realize you are feeling much healthier overall. Thank you for reading!
References
Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Aug 15;48(4):677-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.052. Epub 2006 Jul 24. PMID: 16904534.
Uribarri, Jaime et al. “Advanced glycation end products in foods and a practical guide to their reduction in the diet.” Journal of the American Dietetic Association vol. 110,6 (2010): 911-16.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2010.03.018
Uribarri J, Cai W, Peppa M, Goodman S, Ferrucci L, Striker G, Vlassara H. Circulating glycotoxins and dietary advanced glycation endproducts: two links to inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007 Apr;62(4):427-33. doi: 10.1093/gerona/62.4.427. PMID: 17452738; PMCID: PMC2645629.
Glushakova O, Kosugi T, Roncal C, Mu W, Heinig M, Cirillo P, Sánchez-Lozada LG, Johnson RJ, Nakagawa T. Fructose induces the inflammatory molecule ICAM-1 in endothelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Sep;19(9):1712-20. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007121304. Epub 2008 May 28. PMID: 18508964; PMCID: PMC2518440.
He Y, Yue Y, Zheng X, Zhang K, Chen S, Du Z. Curcumin, inflammation, and chronic diseases: how are they linked? Molecules. 2015 May 20;20(5):9183-213. doi: 10.3390/molecules20059183. PMID: 26007179; PMCID: PMC6272784.




